Analysis of Core Properties and Diversified Applications of Transparent Conductive Films
2025/12/26
0
I. Core Performance Indicators of Transparent Conductive Films
The performance of transparent conductive films directly determines their application suitability. The core indicators can be summarized into the following five points, and an optimal solution must be found in the trade-off between “transparency” and “conductivity”:
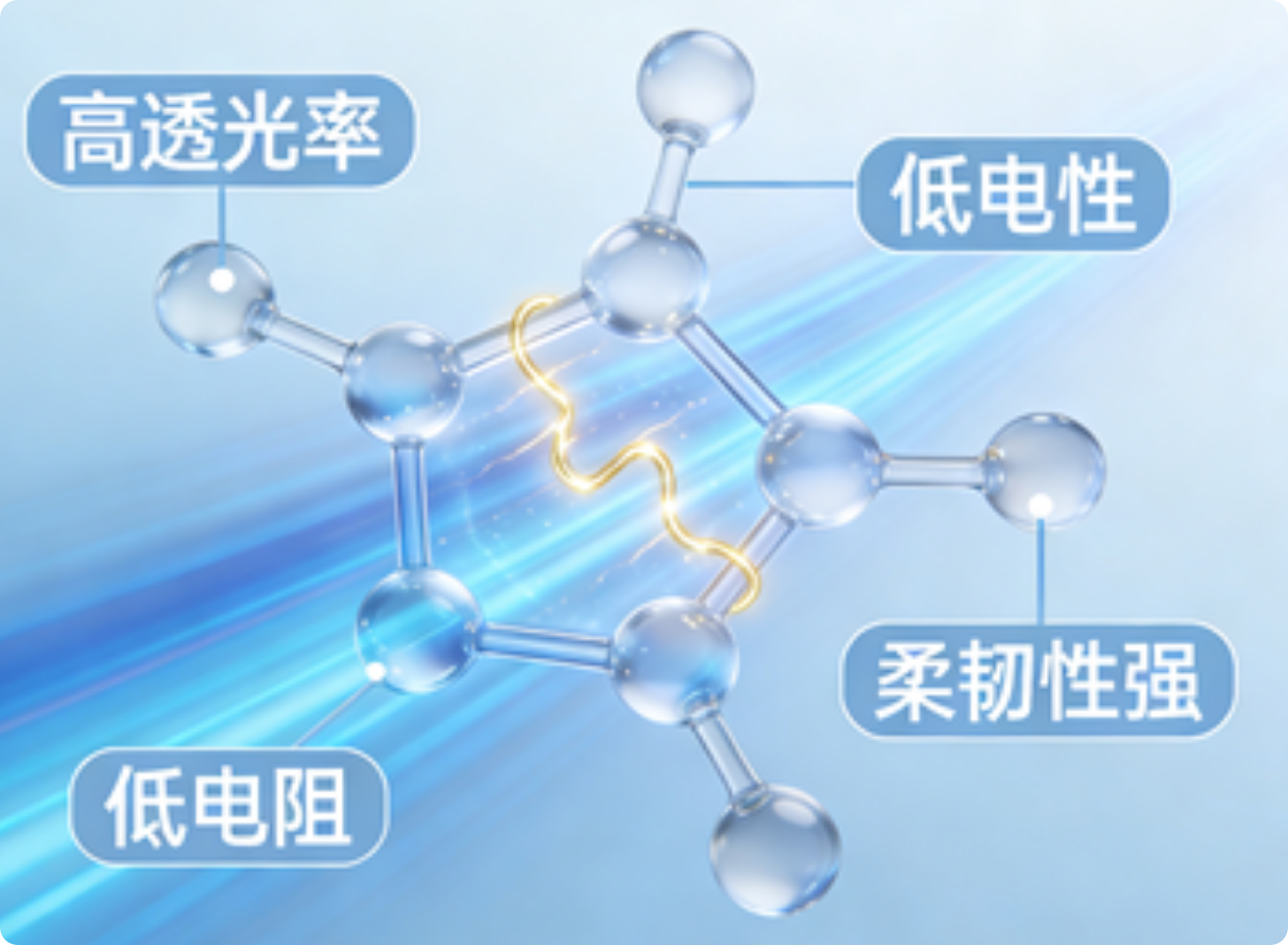
Core Properties and Diversified Applications of Transparent Conductive Films
-
Light Transmittance Performance: Visible light transmittance (400–760 nm) serves as the core indicator. High-quality products typically have a transmittance of ≥ 85%, while high-end display applications require ≥ 90%. Meanwhile, haze must be controlled at ≤ 1% to prevent light scattering from affecting display quality. In addition, the transmittance selectivity in the infrared/ultraviolet bands can be customized according to application scenarios (e.g., photovoltaic applications require enhanced infrared transmittance).
-
Conductivity Performance: Measured by sheet resistance, with the unit of Ω/□ (ohms per square). Conventional applications require sheet resistance ≤ 100 Ω/□, whereas high-end scenarios such as touch displays and flexible electronics demand ≤ 10 Ω/□. Attention should also be paid to the uniformity of sheet resistance (deviation ≤ ±5%) to avoid functional failure caused by local conductivity differences.
-
Mechanical Stability: Including flexibility, wear resistance, and adhesion. For flexible applications (e.g., foldable screens, flexible photovoltaics), the film must withstand repeated 180° bending (bending radius ≤ 5 mm) without cracking, have a surface hardness of ≥ 3H (pencil hardness test), and achieve 5B adhesion rating (cross-cut test) to resist friction and stress during use.
-
Environmental Stability: The film must endure extreme environments such as high and low temperatures (-40℃ ~ 85℃) and damp heat (60℃/90% RH for 1000 hours), with a resistance change rate ≤ 10%, to prevent performance degradation due to oxidation and corrosion. Special scenarios (e.g., outdoor electronics) also require UV aging resistance.
-
Other Key Performance Metrics: Including surface flatness (roughness Ra ≤ 1 nm), chemical corrosion resistance (withstanding acid, alkali, and organic solvent wiping), and optical refractive index matching (reducing interface reflection). Supplementary requirements can be added based on specific application scenarios.
II. Mainstream Application Scenarios of Transparent Conductive Films
With their unique dual properties of “transparency + conductivity”, transparent conductive films have become core materials for multiple strategic emerging industries. Typical applications are as follows:
-
Display and Touch Sectors (Core Applications)
- Smartphones and Tablets: Used as transparent conductive layers for touch electrodes and display panels, requiring high transmittance (≥ 92%), low resistance (≤ 15 Ω/□), and flexibility for foldable screens.
- Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) and Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLED): Applied in pixel driving electrodes and common electrodes, requiring a balance between conductivity uniformity and optical clarity.
- Automotive Displays and Smart Wearables: Need to meet high-temperature stability and scratch resistance requirements, and be compatible with curved surface designs.
-
New Energy Sector
- Photovoltaic Cells: Served as transparent electrodes to collect photogenerated carriers, requiring high transmittance (≥ 88%), low series resistance, and enhanced infrared transmittance to increase power generation. They are mainly used in thin-film photovoltaics (e.g., CIGS, perovskite cells).
- Transparent Conductive Glass (TCG): Utilized in solar water heaters and building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), requiring a combination of transparency, conductivity, and structural strength.
- Lithium-ion Batteries: Some flexible batteries adopt transparent conductive films as current collectors to reduce weight and improve energy density.
-
Electronics and Smart Devices
- Flexible Electronics: Such as flexible sensors and wearable devices, relying on the films’ flexibility and transparency to achieve device miniaturization and morphological diversification.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding: Transparent conductive films can replace metal shielding layers to block electromagnetic interference while maintaining device transparency, which is applicable to medical equipment and precision electronic instruments.
- Transparent Heating Films: Utilize the Joule effect to achieve low-temperature defogging/deicing, applied in automotive windshields, smart mirrors, and medical device lenses.
-
Other Emerging Applications
- Transparent Antennas: Used in 5G communications and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to realize “invisible antenna” design without affecting device appearance.
- Quantum Dot Displays and Micro-LED: As electrode materials for high-end displays, requiring higher conductivity efficiency and optical purity.
- Biomedicine: For example, transparent electrodes are used in cell sensing and biological detection chips, which need to have biocompatibility and high sensitivity.
III. Comparison of Mainstream Transparent Conductive Film Materials (Performance-Application Suitability)
| Material Type | Representative Material | Light Transmittance (%) | Sheet Resistance (Ω/□) | Mechanical Flexibility | Core Advantages | Typical Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxide-based | ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) | 85–90 | 5–20 | Moderate | Mature technology, balanced conductivity and transparency | Traditional displays, touch panels, photovoltaics |
| Oxide-based | AZO (Aluminum-doped Zinc Oxide) | 88–92 | 10–30 | Good | Indium-free and environmentally friendly, low cost | Thin-film photovoltaics, mid-to-low-end displays |
| Carbon-based | Graphene (Single-layer) | 97–98 | 100–300 | Excellent | Ultra-high transparency, extreme flexibility | Flexible electronics, wearable devices |
| Carbon-based | CNT (Carbon Nanotubes) | 85–90 | 50–150 | Excellent | Excellent bending resistance, high stability | Foldable screens, flexible sensors |
| Metal-based | Metal Grids (Ag/Cu) | 80–85 | 1–5 | Good | Outstanding conductivity, controllable cost | Large-size displays, automotive touch systems |
| Polymer-based | PEDOT:PSS (Conductive Polymer) | 85–90 | 50–200 | Excellent | Solution-processable film formation, strong flexible compatibility | Flexible photovoltaics, bioelectronics |
| Composite-based | ITO/Graphene Composite | 90–93 | 5–10 | Good | Balances high conductivity and flexibility | High-end foldable screens, precision electronics |
Note: ITO remains the most widely used material at present, but indium resources are scarce and ITO has high brittleness. New materials such as graphene and carbon nanotubes have greater potential in flexibility and environmental protection, and are the core directions for future technological upgrading.
Dongguan Yusheng Technology specializes in the R&D, development and production of transparent conductive film products. Customization!
















