Application of Conductive Fluororubber in US Military Standard Electronic Products
2026/01/08
0
I. Core Compliance Standards: The Decisive Role of MIL-DTL-83528
The core basis for conductive fluorosilicone rubber to enter the U.S. military specification (Military Specification) electronic product supply chain is MIL-DTL-83528 General Specification for Conductive Elastomers, which covers full-dimensional requirements from material properties to finished product forms:
- Scope of Application: It clearly stipulates that conductive fluorosilicone rubber shall be made into gaskets, O-rings, extrusions, etc., for electromagnetic shielding (EMI/RFI) and sealing protection of electronic equipment.
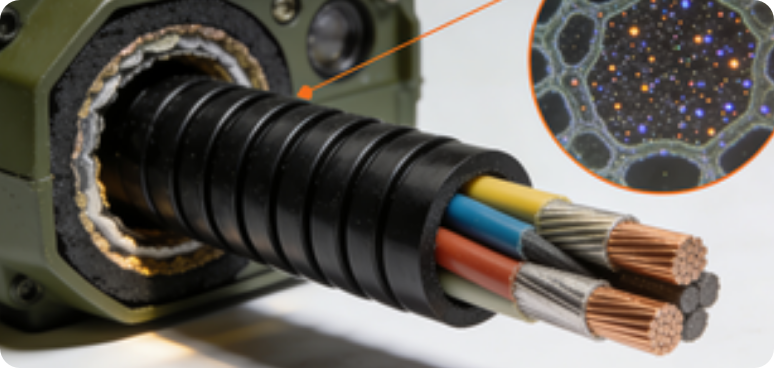
- Key Derivative Standards: Some products need to be linked with subdivided specifications such as MIL-W-22759E (Standard for Fluoropolymer-Insulated Wires). For example, the wire shielding layer must simultaneously meet the conductivity requirements of fluorosilicone rubber and the chemical resistance requirements of the insulation layer.
II. Mandatory Performance Indicators and Typical Data of U.S. Military Specifications
Conductive fluorosilicone rubber that meets the standard must pass multi-dimensional limit tests. an example, the core indicators are as follows:
| Performance Category | Standard Requirement | Typical Measured Value | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Volume Resistivity ≤ 0.010 Ω·cm | 0.002 Ω·cm | MIL-DTL-83528 |
| Shielding Effectiveness | 20MHz–10GHz ≥ 110dB | >125dB | MIL-DTL-83528 |
| Mechanical Properties | Tensile Strength ≥ 180psi | 440psi | ASTM D412 |
| Temperature Resistance | Operating Temperature: -55℃ ~ 125℃ | -65℃ ~ 125℃ | ASTM D1329 |
| Environmental Stability | Deformation ≤ 35% after 70h compression at 100℃ | 24% | ASTM D395B |
| Anti-Interference | Resistivity ≤ 0.015 Ω·cm after EMP Shock | 0.008 Ω·cm | MIL-DTL-83528 |
III. Typical Application Scenarios in U.S. Military Specification Electronic Products
Electromagnetic Shielding and Sealing
At the casing joints of equipment such as radars and communication radios, conductive fluorosilicone rubber gaskets are required to achieve dual protection: they block electromagnetic leakage with a shielding effectiveness of ≥ 110dB (meeting the electromagnetic compatibility requirements of MIL-STD-461), and resist corrosion by fuel and solvents in battlefield environments through the chemical resistance of fluorosilicone rubber. For example, SSP’s die-cut gaskets have been used in U.S. military airborne electronic countermeasure systems.
Precision Circuit Connection
In microelectronic devices such as missile guidance modules, anisotropic conductive film (ACF) made of conductive fluorosilicone rubber can achieve low-impedance connection between chips and substrates in a narrow space, while withstanding extreme temperature differences of -55℃ ~ 125℃.
Wire Shielding Enhancement
Cooperating with fluoropolymer-insulated wires that comply with the MIL-W-22759E standard, conductive fluorosilicone rubber is used as a shielding layer filler, which can improve the anti-interference ability of wires in strong electromagnetic environments such as radar stations. Its volume resistivity stability (still reaching 0.0004 Ω·cm after 1000 hours of aging) is far superior to ordinary conductive rubber.
IV. Key Certification and Selection Processes
Compliance Certification Path
The U.S. military specification certification process must be strictly followed:
- Lock the Corresponding Model of MIL-DTL-83528 (e.g., Type C is for fluorosilicone-based conductive materials);
- Entrust Institutions Such as EUROLAB to complete environmental adaptability (high and low temperature, salt spray), mechanical stress (vibration, impact), and electrical performance (EMC) tests;
- Submit the Test Report to DLA (Defense Logistics Agency). After passing the review, it will be included in the QPL (Qualified Products List)
Core Selection Considerations
- Filler Matching: Prioritize inert filler systems such as silver-plated copper and nickel-coated graphite to avoid metal ion migration during vulcanization affecting circuit accuracy;
- Molding Process Adaptation: Extrusions are suitable for long strip sealing grooves, and die-cut parts are suitable for complex-shaped casings. Selection shall be based on equipment drawings;
- Fluid Compatibility: If it comes into contact with aviation fuel, additional volume swelling rate tests are required (≤ 25% is qualified).