Application of PDMS in Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
I. Fundamental Technical Compatibility of PDMS and VSD
- Biocompatibility: Certified to ISO 10993, non-toxic and non-irritating, it can directly contact wound tissue and avoid inflammatory reactions caused by traditional materials.
- High-efficiency Hermeticity: Boasting excellent elasticity and surface conformability, it can tightly adhere to skin contours, maintain a stable negative pressure environment of -125~-450mmHg, and reduce the risk of air leakage.
- Chemical Stability: Resistant to acid, alkali and body fluid corrosion, it can maintain stable performance for a long time in the environment of wound exudate and irrigation fluid, with a service life extended by more than 30% compared with traditional polyurethane materials.
- Processing Flexibility: It can be fabricated into complex structures via soft lithography, 3D printing and other technologies, enabling functional integration.
II. Three Core Application Scenarios of PDMS in VSD
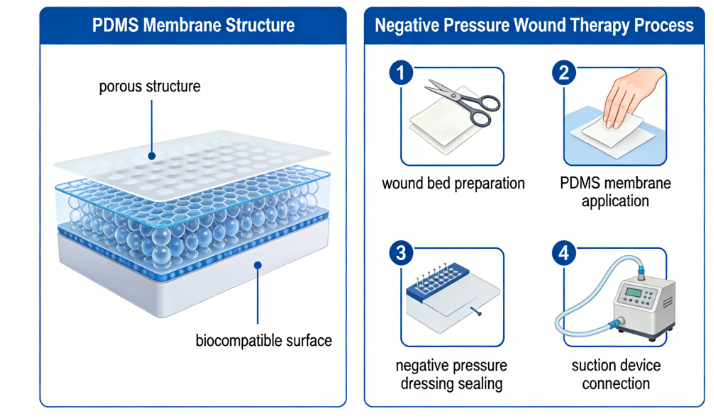
1. Manufacturing of Negative Pressure Sealing Membranes and Drainage Tubing
Core Function: Serving as the “hermetic barrier” of the VSD system, the PDMS sealing membrane forms a hydrophobic surface via methyl groups, which not only prevents the invasion of external bacteria but also reduces seal failure caused by sweat accumulation. Its temperature resistance range of -65℃ to 315℃ is compatible with clinical disinfection requirements.
Technological Upgrade: Jiangsu Pulus Biotechnology Co., Ltd. has increased the purity of PDMS to 99.9% through a multi-stage rectification and purification process. The ultra-thin sealing membrane (thickness < 0.1mm) produced features both flexibility and tear resistance, and does not restrict patients’ movement when attached to movable parts such as joints.
2. Integration of Intelligent Wound Monitoring Components
Pressure Sensing Function: PDMS is compounded with conductive materials such as carbon nanotubes and graphene to prepare flexible pressure sensors, which are embedded in VSD dressings to monitor the changes in wound negative pressure in real time and achieve precise pressure control (error < 5mmHg) through electrical signal feedback.
**Exudate Analysis Module**: Utilizing the high permeability and chemical inertness of PDMS, a microfluidic chip-type exudate collection channel is developed. Combined with its light transmittance (light transmittance > 90%), the concentration of inflammatory factors in exudate can be detected in real time through spectral analysis to early warn of infection risks.
3. Auxiliary Carrier for Wound Repair
Drug Sustained-Release Platform: Porous PDMS scaffolds are prepared by 3D printing technology to load growth factors or antibacterial drugs, realizing local sustained release in a negative pressure environment (the drug release cycle can reach 7-14 days), which solves the limitation of traditional VSD with only drainage function and no active treatment.
Tissue Regeneration Scaffold: PDMS microporous platforms (such as the V-bottom microporous structure developed by Jinan University) can induce the generation of vascular organoids. When integrated into VSD dressings, it can promote the regeneration of microvessels in wounds and accelerate the healing of ischemic wounds.
III. Comparison of Technical Advantages of PDMS-Enabled VSD
| Performance Dimension | PDMS-based VSD Components | Traditional Polyurethane Components | Advantage Improvement Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hermeticity Retention Time | 7-10 days | 3-5 days | 80% |
| Biocompatibility | ISO 10993 Certified | Prone to contact dermatitis | — |
| Functional Expandability | Integratable with sensing and drug release functions | Single drainage function | — |
| Disinfection Resistance | Resistant to high-temperature and high-pressure sterilization | Only compatible with ethylene oxide disinfection | — |
IV. Application Limitations and Future Directions
Existing Challenges: The high air permeability of PDMS may lead to excessive evaporation of wound moisture, requiring the optimization of moisturizing performance through composite hydrogel coatings.
Development Trend: Combining degradable PDMS technology (e.g., PDMS/PBSA copolymers), develop integrated bioabsorbable VSD dressings with drainage, monitoring and drug delivery functions to further shorten the wound healing cycle.