Applications of Garment Silicone in the Apparel Field
Definition of Garment Silicone
Garment silicone is a type of silicone material specifically designed for the apparel industry. It is primarily composed of siloxane, with the addition of auxiliary materials such as reinforcing agents, cross-linking agents, and catalysts, and is processed through specific techniques. It exhibits excellent elasticity, resistance to high and low temperatures, aging resistance, water resistance, and strong adhesion to fabrics. It can realize various functional and decorative effects on clothing, providing crucial support for the innovative development of the apparel industry.

Applications of Garment Silicone in the Apparel Field
II. Applications of Garment Silicone in the Apparel Field
(I) Decorative Applications
Pattern Printing: Through processes like screen printing and transfer printing, various vivid, three-dimensional patterns (such as cartoon characters, geometric shapes, and brand logos) can be printed on clothing surfaces. These patterns not only retain their color for a long time and are resistant to fading but also have a soft texture that does not affect the wearing comfort of the garment. They are widely used on T-shirts, hoodies, sportswear, and other types of clothing to enhance the garment’s aesthetics and brand recognition.
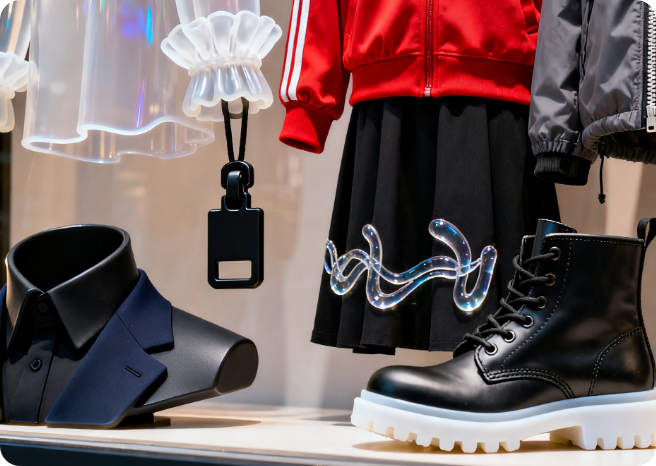
Three-Dimensional Styling: Leveraging the plasticity of silicone, various three-dimensional structures (such as 3D flowers, bows, and badges) can be created and attached to clothing. These 3D elements have a strong visual impact, making the garment more personalized and fashionable. They are commonly used in women’s clothing, children’s clothing, and stage costumes.
(II) Functional Applications
Anti-Slip: By coating or printing a layer of garment silicone on specific parts of clothing (e.g., cuffs, necklines, trouser hems, and the joint between the upper and sole of sports shoes), friction at these parts can be effectively increased to achieve an anti-slip effect. For example, the anti-slip silicone design on the cuffs and trouser hems of sportswear prevents the garment from shifting during exercise, ensuring movement flexibility; the anti-slip silicone stripes on the upper of sports shoes enhance the fit between the shoe and the foot, improving sports safety.
Waterproof: When made into a waterproof coating and applied to the surface of garment fabrics, garment silicone forms a waterproof film that blocks water penetration, endowing the garment with waterproof functionality. Such waterproof clothing is suitable for wearing in rainy or humid environments, such as outdoor jackets and raincoats. Meanwhile, this waterproof coating also has good breathability, which does not affect the wearing comfort of the garment and avoids the drawback of poor breathability in traditional waterproof clothing.
Thermal Insulation: Some types of garment silicone have excellent heat insulation properties. When applied to the interlayer or lining of clothing, they form a heat-insulating layer that reduces heat loss from the body, thereby achieving a thermal insulation effect. For instance, adding silicone thermal strips to heat-prone areas of winter clothing (such as necklines, cuffs, and hems) can effectively enhance the garment’s warmth retention, keeping people warm even in cold weather.
(III) Protective Applications
Abrasion Resistance: Reinforcing high-wear areas of clothing (e.g., knees, elbows, and hips) with garment silicone can improve the abrasion resistance of these parts and extend the garment’s service life. For example, work pants often have silicone anti-abrasion patches on the knee areas, making them more suitable for use in harsh working environments; children’s clothing also adopts silicone protective designs on elbows and knees to prevent garment wear when children play.
Scald Resistance: For special-purpose clothing (such as chef uniforms and fire-resistant clothing), high-temperature-resistant garment silicone is used on parts like cuffs and necklines to provide a certain level of scald resistance. When these parts come into contact with high-temperature objects, the silicone material blocks the rapid transfer of heat to the skin, providing a certain amount of protection time for the human body.
III. Types of Garment Silicone
(I) Classification by Form
Liquid Garment Silicone: It is in a liquid state, with good fluidity and permeability. It can be applied to clothing surfaces through various processes such as brushing, dipping, spraying, and screen printing. It bonds fully with garment fabrics to form a uniform coating or pattern, and after drying and curing, it exhibits good elasticity and adhesion. Liquid garment silicone is often used for pattern printing, waterproof coating production, and anti-slip treatment of clothing.
Solid Garment Silicone: It usually exists in the form of sheets, strips, or blocks, with fixed shapes and sizes. It can be attached to clothing through cutting, pasting, or sewing, and is mainly used for creating 3D styles on clothing, as well as making anti-slip strips and anti-abrasion patches. The hardness and elasticity of solid garment silicone can be adjusted according to requirements to meet different application needs.
(II) Classification by Function
Decorative Garment Silicone: Focused on enhancing the aesthetic decoration of clothing, it comes in a wide range of colors and can be made into various patterns and 3D structures. It has good color stability and glossiness. Examples include colored liquid silicone for garment printing and solid silicone for making 3D decorative elements.
Functional Garment Silicone: Primarily designed to achieve specific functions. According to different functions, it can be further divided into anti-slip garment silicone, waterproof garment silicone, thermal insulation garment silicone, abrasion-resistant garment silicone, high-temperature-resistant/scald-resistant garment silicone, etc. While providing corresponding functions, this type of silicone also maintains a certain level of adhesion and durability.
(III) Classification by Vulcanization Method
Room-Temperature Vulcanizing (RTV) Garment Silicone: It undergoes vulcanization at room temperature and can cure and form without heating or with only slight heating. It is easy to use and operate, making it suitable for small-scale production or on-site construction (e.g., local repair of clothing and printing of small patterns).
High-Temperature Vulcanizing (HTV) Garment Silicone: It requires vulcanization and curing at relatively high temperatures (usually 100-200°C). It has a relatively fast curing speed and excellent physical and chemical properties (e.g., high strength, good aging resistance, and strong high-temperature resistance). HTV garment silicone is suitable for large-scale industrial production and is widely used in garment silicone products with high performance requirements, such as waterproof coatings and anti-abrasion patches.
IV. Usage Methods of Garment Silicone
(I) Usage Method of Liquid Garment Silicone
Preparation Work: First, clean the garment fabric to be processed to remove surface impurities such as dust and oil, ensuring the fabric is dry and flat. Then, prepare appropriate tools (e.g., screens, scrapers, and molds) according to design requirements. Stir the liquid garment silicone evenly; if color adjustment is needed, add an appropriate amount of silicone-specific color paste and mix thoroughly until the color is uniform.
Coating/Printing Operation:
Brushing Method: Use a brush or scraper to evenly apply the liquid silicone to the designated area of the garment fabric. Control the coating thickness according to requirements (usually 0.1-0.5mm). During brushing, avoid air bubbles and sagging to ensure the coating is flat and smooth.
Screen Printing Method: Fix the screen with the designed pattern on the printing table, lay the garment fabric flat under the screen, and pour the liquid silicone into the pattern area of the screen. Use a scraper to scrape evenly at a certain angle and force, allowing the silicone to transfer to the garment fabric through the mesh of the screen. After printing, carefully remove the screen and inspect the printed pattern, repairing any defects promptly.
Curing Treatment: Place the garment with the coated or printed silicone in a well-ventilated environment. Room-temperature vulcanizing silicone can be cured by natural placement; the curing time varies depending on the silicone type and ambient temperature, usually ranging from several hours to more than ten hours. High-temperature vulcanizing silicone needs to be baked and cured in an oven at a specified temperature, with a curing time typically of 10-30 minutes. During curing, control the temperature and time carefully to prevent silicone aging or discoloration caused by excessively high temperature or prolonged time, which would affect product quality.
Post-Processing: After the silicone is fully cured, inspect the garment, remove excess silicone or burrs, and perform subsequent treatments (such as washing and ironing) if necessary to meet the final product requirements of the garment.
(II) Usage Method of Solid Garment Silicone
Cutting and Processing: According to the design size and shape of the garment, use scissors or special cutting equipment to cut solid garment silicone sheets, strips, etc., into the required shape. Ensure the cut edges are neat and the size is accurate to avoid deviations.
Attachment and Fixation:
Adhesion Method: Apply an appropriate amount of silicone-specific adhesive to the back of the solid silicone, then accurately stick it to the designated position on the garment fabric. Gently press with hands or a roller to ensure tight bonding between the silicone and the fabric, and let the adhesive cure for a period of time to ensure the silicone is firmly attached.
Sewing Method: For large solid silicone products or those requiring strong adhesion, sewing can be used to fix them to the garment. Pre-punch holes along the edge of the silicone product, then sew it to the garment fabric with needles and threads. During sewing, ensure even stitches to avoid damaging the silicone product and the garment fabric.
Inspection and Trimming: After attachment and fixation, check whether the silicone product is correctly positioned on the garment and whether its adhesion is firm. Adjust and repair promptly if there is looseness or position deviation. Meanwhile, trim the thread ends at the sewing positions to keep the garment’s appearance neat and attractive.
V. Precautions for Using Garment Silicone
(I) Selecting the Appropriate Garment Silicone
Choose the type of garment silicone based on the garment’s usage scenario and functional requirements. For example, outdoor waterproof clothing should use garment silicone with excellent waterproof performance; the anti-slip parts of sportswear should use silicone with good anti-slip effect and elasticity; children’s clothing should use non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and soft silicone products to ensure children’s wearing safety and comfort.
Consider the characteristics of the garment fabric, as different fabrics may have varying adhesion to silicone. Before large-scale application, it is advisable to conduct a small-area test on the edge of the garment fabric to check the adhesion effect between the silicone and the fabric, the hand feel after curing, and whether the fabric is damaged (e.g., discoloration, deformation). Proceed with large-scale use only after confirming suitability.
(II) Precautions During Operation
During the use of liquid garment silicone, avoid mixing in impurities, as this will affect the curing effect and performance of the silicone. Use clean containers and tools when stirring the silicone, and ensure a clean working environment during brushing or printing. Additionally, liquid silicone has a certain degree of volatility; maintain good ventilation during operation to avoid long-term inhalation of silicone volatile substances, which may harm the human body.
When conducting high-temperature vulcanization and curing, strictly control the oven temperature and time in accordance with the silicone’s curing process requirements. Excessively high temperatures may cause silicone decomposition and discoloration, while excessively low temperatures will result in incomplete curing of the silicone, affecting product quality. Pay attention to safety when putting in and taking out the garment to avoid scalding.
When using adhesive to stick solid silicone, select a special adhesive compatible with both the silicone and the garment fabric. Avoid using ordinary adhesives, which may cause the silicone to fall off or damage the fabric. Apply an appropriate amount of adhesive: excessive adhesive may overflow and affect the garment’s appearance, while insufficient adhesive will lead to poor adhesion.
(III) Storage and Maintenance
Store garment silicone in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated environment, avoiding direct sunlight, high-temperature exposure, and contact with fire sources and corrosive substances. Liquid silicone should be sealed to prevent volatilization and moisture absorption; solid silicone should be protected from extrusion and impact to avoid deformation or damage.
For garments with silicone components, pay attention to the water temperature when washing. It is generally recommended to wash with cold or warm water; avoid using high-temperature hot water, as this may cause the silicone to age, deform, or fall off. Meanwhile, avoid using strongly alkaline or oxidizing detergents to prevent silicone corrosion, which would affect its performance and appearance. After washing, air-dry the garment naturally; do not expose it to direct sunlight or use a dryer.
VI. Development Trends of Garment Silicone
With the continuous improvement of people’s demands for garment quality and personalization, and the advancement of technology, garment silicone will show the following development trends in the future:
Functional Diversification: Future garment silicone will no longer be limited to a single decorative purpose or a single function but will develop toward multi-functional integration. For example, a type of garment silicone may have both waterproof and anti-slip functions, as well as thermal insulation and antibacterial effects, meeting people’s diverse needs for clothing.
Environmental Friendliness: With the enhancement of environmental awareness, eco-friendly garment silicone will become the mainstream development direction. Researchers will continue to explore new eco-friendly materials and production processes to reduce pollution emissions during silicone production, while ensuring that silicone products are harmless to the human body and the environment during use and can be easily degraded or recycled after disposal.
Intelligence: By integrating intelligent technology, garment silicone will be combined with sensors, conductive materials, and other components to develop intelligent garment silicone products. For instance, intelligent garment silicone patches that can monitor physiological indicators (such as body temperature and heart rate) or intelligent decorative silicone that can realize light-emitting and color-changing effects will make clothing more intelligent and personalized, bringing more convenience and fun to people’s lives.
Lightweight and Ultra-Thin Design: To improve the wearing comfort of clothing, future garment silicone will develop toward lightweight and ultra-thin designs. By optimizing material formulas and production processes, the density and thickness of silicone will be reduced while ensuring its performance, making clothing lighter and softer and enhancing the wearing experience.