Application of Thermal Conductive Shielding Adhesive Film in Electronic Chips
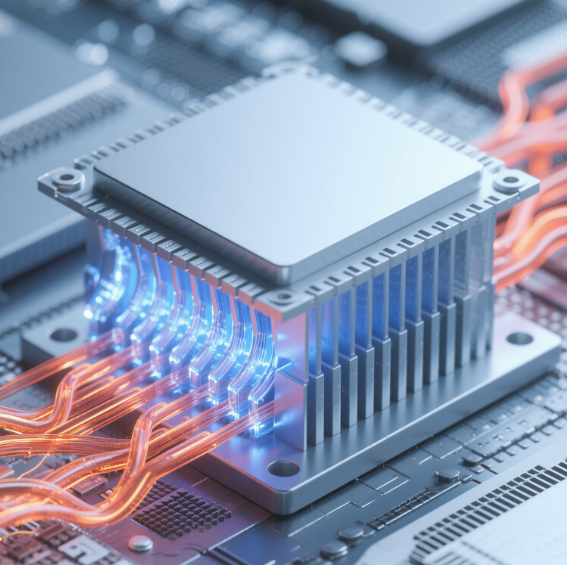 In the current context of the rapid development of the electronic information industry, the integration degree and operating speed of electronic chips are constantly increasing, and the heat dissipation and electromagnetic interference problems they face have become more and more severe. With its excellent thermal conductivity and electromagnetic shielding capabilities, the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film has become a core material for solving the key problems of electronic chips and plays an irreplaceable role in the field of electronic chips.
In the current context of the rapid development of the electronic information industry, the integration degree and operating speed of electronic chips are constantly increasing, and the heat dissipation and electromagnetic interference problems they face have become more and more severe. With its excellent thermal conductivity and electromagnetic shielding capabilities, the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film has become a core material for solving the key problems of electronic chips and plays an irreplaceable role in the field of electronic chips.
Characteristics of Thermal Conductive Shielding Adhesive Film
The thermal conductive shielding adhesive film is a functional composite material that skillfully combines the characteristics of thermal conductive materials and electromagnetic shielding materials. In terms of thermal conductivity, the adhesive film is filled with fillers with high thermal conductivity coefficients, such as ceramic particles like aluminum oxide and boron nitride. These fillers construct an efficient heat conduction path, enabling the adhesive film to have good thermal conductivity and quickly transfer the heat generated by the chip. In terms of electromagnetic shielding, metal powders, metal fibers, or conductive polymer materials are added to the adhesive film. These substances interweave with each other to form a continuous conductive network, which can effectively reflect, absorb, and scatter electromagnetic waves, thus achieving the shielding of electromagnetic interference. At the same time, the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film also has good flexibility, adhesion, and processing performance. It can be customized according to the shapes and sizes of different chips, making it convenient for installation and use.
Solving the Chip Heat Dissipation Problem
During the operation of electronic chips, components such as transistors continuously convert and process electrical signals, generating a large amount of heat. If this heat cannot be dissipated in a timely manner, the temperature of the chip will continue to rise, leading to a decline in chip performance and even thermal failure. The thermal conductivity characteristics of the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film play a key role here. When the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film is applied between the chip and the heat dissipation device (such as a heat sink or radiator), it can closely adhere to the surface of the chip and the heat dissipation device, eliminating the air gap. The thermal conductivity coefficient of air is extremely low, and it is a poor conductor of heat transfer. When the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film replaces the air, it greatly reduces the thermal resistance, allowing the heat to quickly transfer from the chip to the heat dissipation device and then be dissipated into the surrounding environment through the heat dissipation device. For example, in the heat dissipation of high-performance CPU chips, after using the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film, the operating temperature of the chip can be reduced by 10°C – 15°C, effectively ensuring the stable operation and service life of the chip.
Addressing the Electromagnetic Interference Problem
With the increasing complexity of the functions of electronic devices, there are a large number of electromagnetic signals around electronic chips. These electromagnetic signals interfere with each other, which will affect the normal operation of the chip, leading to problems such as data transmission errors and signal distortion. The electromagnetic shielding function of the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film can build an electromagnetic protection barrier for the chip. When electromagnetic waves encounter the conductive network in the adhesive film, part of the electromagnetic waves will be reflected back into space by the conductive network, and another part of the electromagnetic waves will generate an induced current in the conductive network. During the flow of the current, it is converted into heat energy due to resistance loss, thus achieving the absorption of electromagnetic waves. Through this dual function of reflection and absorption, the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film can reduce the electromagnetic interference around the chip to the lowest level, ensuring the accuracy and stability of the chip’s signal transmission. In 5G communication chips, due to their high operating frequency bands and fast data transmission rates, the requirements for electromagnetic shielding are more stringent. After using the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film, the signal transmission quality of the chip has been significantly improved, and the bit error rate has been greatly reduced.
Other Application Advantages
In addition to the functions of heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding, the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film also has insulating properties, which can prevent short circuits between the chip and other components and improve the safety of electronic devices. At the same time, its good adhesion can firmly connect the chip with components such as the heat dissipation device and the circuit board, enhancing the structural stability of the electronic device. In some miniaturized and thin-and-light electronic devices, such as smartphones and tablets, the flexibility of the thermal conductive shielding adhesive film enables it to adapt to the complex internal structure, achieving efficient heat dissipation and shielding and meeting the development needs of electronic devices that are constantly pursuing thinness, lightness, and portability.
Application Prospects and Challenges
With the continuous development of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and big data, higher requirements have been put forward for the performance and reliability of electronic chips, and the market demand for thermal conductive shielding adhesive films will also continue to grow. In the future, thermal conductive shielding adhesive films will develop towards higher thermal conductivity coefficients, stronger electromagnetic shielding efficiency, thinner thicknesses, and more environmental friendliness. However, currently, thermal conductive shielding adhesive films still face some challenges during the application process, such as higher costs and the performance stability after long-term use. Researchers need to continuously explore new materials and preparation processes to reduce costs, improve performance, and further expand the application of thermal conductive shielding adhesive films in the field of electronic chips.